Research
My research interests focus on the clinical science of multiple sclerosis - the commonest potentially disabling disease of young adults. The research group has a broad set of interests: we work on the aetiology through international collaborations in genetics involving large-scale whole genome screening for factors that confer susceptibility and influence disease progression; in neurobiology, we study interactions between glia and axons, and the potential role of human stem cells as 'medicines' for limiting and the repairing the damage; our work in therapeutic immunology has used the monoclonal antibody Campath-1H (licensed as Lemtrada in 2013) to treat patients with active relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and to understand mechanisms of tissue injury involved in the complex pathogenesis of the disease.
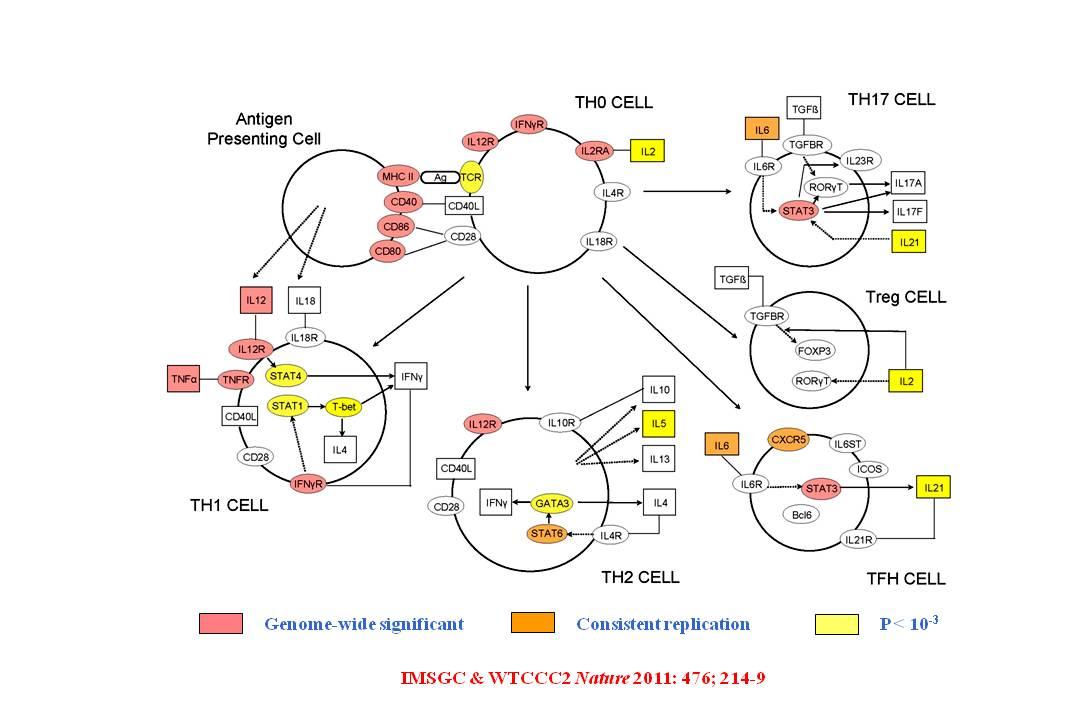
Graphical representation of the T helper cell differentiation pathway. Alpha-numeric labels indicate the individual genes and gene complexes (nodes) included in the pathway (note some are included more than once). Coloured nodes are those containing a gene implicated by proximity to a SNP showing evidence of association. Red:have genome-wide significance; Orange: other loci or discovery P value < 1×10−4.5 and consistent replication data. Yellow: Discovery P value < 1×10−3. Other molecules (proteins, vitamins etc.) may also be of relevance in these processes but are not included here as they are not currently listed as being part of this particular pathway in the IPA database.
Publications
Jones JL, Thompson SA, Loh P, Davies JL, Tuohy OC, Curry AJ, Azzopardi L, Hill-Cawthorne G, Fahey MT, Compston A, Coles AJ. Human autoimmunity after lymphocyte depletion is caused by homeostatic T-cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013: 110; 20200-5
Cohen JA, Coles AJ, Arnold DL, Confavreux C, Fox EJ, Hartung H-P, Havrdova E, Selmaj KW, Weiner HL, Fisher E, Brinar VV, Giovannoni G, Stojanovic M, Ertik BI, Lake SL, Margolin DH, Panzara MA, Compston DAS for the CARE-MS I investigators. Alemtuzumab versus interferon beta 1a as first-line treatment for patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012: 380; 1819-28
Coles AJ, Twyman CL, Arnold DL, Cohen JA, Confavreux C, Fox EJ, Hartung H-P, Havrdova E, Selmaj KW, Weiner HL, Miller T, Fisher E, Sandbrink R, Lake SL, Margolin DH, Oyuela P, Panzara MA, Compston DAS for the CARE-MS II investigators. Alemtuzumab for patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis after disease-modifying therapy: a randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012: 380; 1829-
The International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (IMSGC) and the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2). Genetic risk and a primary role for cell-mediated immune mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature 2011: 476; 214-219
International CAMMS223 Trial Study Group. A randomized, rater-blinded, trial of alemtuzumab versus interferon beta-1a in early, relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2008: 359; 1786-1801
The International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium. Novel Risk Alleles for Multiple Sclerosis Identified by a Whole Genome Association Study. New England Journal of Medicine 2007: 357; 851-862



